Aphakia
|
||
|
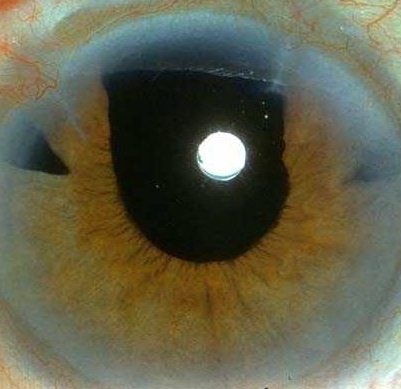
The patient has a cataract extraction without lens implant (examine the wound to see if this is done through phacoemulsification or otherwise). The patient may be wearing thick lenses or contact lenses. In intracapsular cataract extraction, there is usually
iridectomy and the presence of vitreous
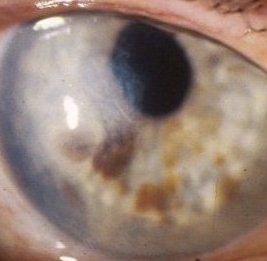
Some patients may have extracapsular cataract extraction
without implant (for example in clear
Others:
anterior chamber and band keratopathy. high myopic patient with aphakia. The clue to the presence of aphakia is the relatively low minus (concave) power on the ophthalmoscope needed to visualize the fundus. |
Questions:
1. What is the average refractive power of the lens?