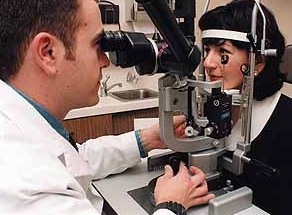
- Learn direct, diffuse illumination, scleral scatter, specular reflection
- Look for iris transillumination
- If asked, formal AC depth measure:
- set slit beam mounting at 60 degrees to microscope
- use horizontal slit beam
- adjust slit beam to join corneal and iris reflections measure slit length and multiply by 1.4 for AC depth in mm.
- pigmented lesions of the bulbar conjunctiva
- deposits on cornea such as ferritin line or pigments on the endothelium
- iris transillumination
- small corneal scar
- peripheral iridotomy
- Montelo's tube
| 1. Check set
up of machine.
2. Observe the patient before examination. Obvious signs
may be missed on
3. Position the patient comfortably. 4. Examine the anterior segments and then the posterior segments unless told otherwise. 5. Remember to examine the fornix (scars, adrenochrome
etc) and superior
6. Special note:
|
|
| Back to the index for final MRCOphth |