 |
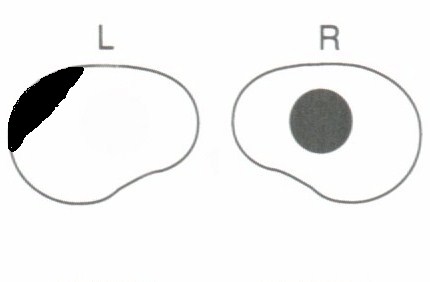
The patient has a right
central scotoma and superior temporal field defect in the left eye. The
findings suggest a lesion in the junction between the optic nerve and the
chiasm on the side with the central scotoma. What is the anatomical explanation
for junctional scotoma?
|