| Materials |
Polyamide (Nylon) |
Silk
|
Polypropylene (eg. prolene)  |
Polyester (eg. Mersilene) |
| Types | *monofilaments |
2 types of fine silk sutures: *virgin silk
*braided silk
Both are multifilaments |
*monofilaments
also available as *multifilaments |
*monofilaments |
| Tissue reaction |
*minimal |
*moderate |
*minimal |
*minimal |
| Tensile strength |
*high, losing 10 to 15% of strength per year |
*moderate, lasting 3 to 6 months |
*high, maintain strength for over 2 years |
*high, permanent |
| Other characteristics | *mild elasticity
*stiff suture ends which
|
*inelastic
*suture ends soft and
|
*most elastic suture materials
*stiff suture ends and irritate
|
*strongest monofilament
and less elasticity than other monofilaments |
| Indications | *most widely suture for
corneal wound sutures |
*rarely used to close corneal
wound sutures but often used as stay sutures. |
* used mainly in iris repair
and intraocular lens fixation |
*prefer by some surgeons
for its low elasticity and high tensile strength |

 magnified
view of monofilament
magnified
view of monofilament 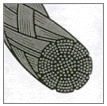 magnified
view of multifilament
magnified
view of multifilament