Lacrimal gland tumour is uncommon outside the referral centre.
However, in the examination you will be expected to know the differences
between the two main types of lacrimal gland tumours: pleomorphic adenoma
and adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Pleomorphic adenoma (also called mixed cell tumour) is slow growing
and has apparent encapsulation (it is not a true capsule but results from
compression of adjacent tissue).
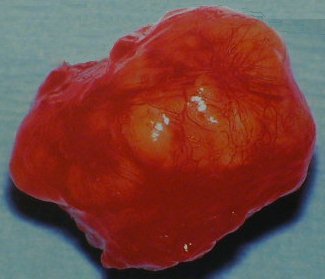
Gross pathology of a pleomorphic adenoma.
The capsule is the result of adjacent tissue compression. |
Histologically, two components are present: the epithelial
and stromal (mesenchymal) components. You are likely to be asked about
the surgical principles in removing this tumour (avoid biopsy to avoid
seeding and
recurrence). Occasionally the tumour may transform into adenocarcinoma.
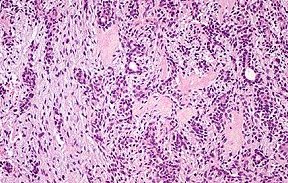
Low magnification of pleomorphic adenoma |
|
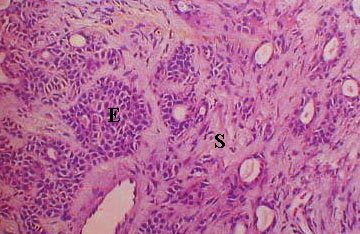
Higher magnification of pleomorphic adenoma showing
the epithelial (E) and the stromal (S) components. |
|
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is the most common malignant tumour
arising from the lacrimal gland tissue. It is an aggressive tumour and
often invades the nerve causing pain and intracranial spread. The histology
may show many patterns but the most characteristic pattern and the most
likely to appear in the examination is that of "Swiss-cheese" pattern.
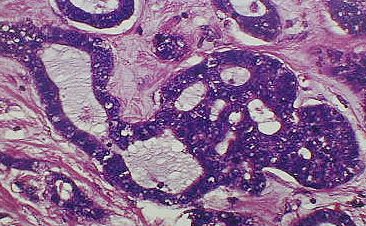
High magnification.
Adenoid cystic carcinoma with Swiss cheese pattern. |
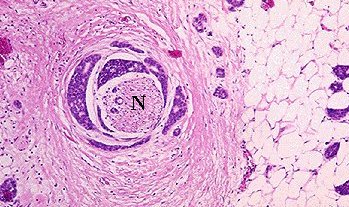
Nerve (N) invaded by adenoid cystic carcinoma
(the blue area surrounding the nerve) |
Common viva questions:
-
Give a differential diagnosis of a lacrimal fossa mass. (While
lacrimal gland tumour should be included in the differential diagnosis,
50% of lacrimal masses will be caused by inflammation such as sarcoidosis
or Sjogren's syndrome and lymphoid infiltration such as lymphoma)
-
How do you differentiate pleomorphic adenoma from adenoid
cystic carcinoma? (History: slow vs rapid; painless vs painful. CT scan:
appear encapsulated vs uncapsulated; bone erosion vs bone destruction)
-
When would you biopsy a lacrimal mass? (Not to be taken
lightly. In pleomorphic adenoma, rupture of capsule causes seeding and
aggressive recurrence.)
-
What is the recommended treatment for lacrimal gland tumours?
(In
pleomorphic adenoma en bloc excision and in adenoid cystic carcinoma exenternation
with removal of adjacent bone.)
|




